This website uses cookies to improve your experience. See our Privacy Policy to learn more.
ALL-
Reliable BIM Services in New York I
3D Laser Scanning I Shop Drawings
3D Laser Scanning I Shop Drawings
CITY SKETCHERS

Discuss a project
Fill out the form below, submit a request and we will contact you shortly
By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
ABOUT US

All-City Sketchers is a seasoned provider of BIM services in New York, New Jersey and other areas.
Since the foundation in 2012, All-City Sketchers have been providing services in the field of BIM engineering, based on more than 20 years experience of the team members.
With the rise of customer needs, ACS began to develop integrated solutions: including 3D Laser Scanning, Scan-to-BIM and BIM Modeling in the performance of work for different trades and coordination between them.
Being among the early pioneers of 3D Modeling and having delivered over 700 successful projects our passionate and diverse team is eager to implement their knowledge in increasingly complex tasks.
We are convinced that our extensive field expertise combined with advanced technology skills will help us to deliver your best project.
Since the foundation in 2012, All-City Sketchers have been providing services in the field of BIM engineering, based on more than 20 years experience of the team members.
With the rise of customer needs, ACS began to develop integrated solutions: including 3D Laser Scanning, Scan-to-BIM and BIM Modeling in the performance of work for different trades and coordination between them.
Being among the early pioneers of 3D Modeling and having delivered over 700 successful projects our passionate and diverse team is eager to implement their knowledge in increasingly complex tasks.
We are convinced that our extensive field expertise combined with advanced technology skills will help us to deliver your best project.
20+
10+
800+
years of team members experience
million sq ft digitized
successful projects
85
happy clients
services


BIM Modeling & Coordination
3D Laser Scanning I
Point Cloud Processing
3D and 2D MEP Shop Drawings
for Fabrication
Transform your project’s vision into an intelligent, clash-free 3D BIM environment. Our expert modeling and coordination services ensure seamless integration of all disciplines, optimize design visualization, and pave the way for efficient construction planning. learn more
Capture reality with unparalleled precision. Our advanced 3D laser scanning and point cloud processing services provide accurate digital twins of existing conditions, even in the most complex spaces. This detailed data is crucial for minimizing construction errors, enabling precise as-built documentation, and facilitating informed decision-making. learn more
Ensure precise fabrication and installation with our detailed MEP shop drawings. Generated directly from your BIM models or scan data, our 2D and 3D drawings minimize errors, reduce rework, and enhance communication across your project team. learn more
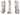
BIM Modeling & Coordination
By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
3D Scanning
By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
Shop Drawings
By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
clients




TRADE CONTRACTORS
Shop Drawings for Fabrication
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination

GENERAL CONTRACTORS
3D Laser Scanning, BIM Pre-Coordination
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination,
BIM Consultant Services
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination,
BIM Consultant Services


DEVELOPERS & OWNERS
3D Laser Scanning, As-built Modeling
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination
BIM Consultant Services
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination
BIM Consultant Services



ARCHITECTS & ENGINEERS
3D Laser Scanning, BIM Pre-Coordination
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination
As-built Modeling
Scan to BIM Modeling, BIM Coordination
As-built Modeling
INDUSTRIES

Commercial & Office

INDUSTRIAL & HEALTHCARE

RESIDENTIAL
ALL-CITY SKETCHERS PRIORITIES

Predictable
Project Timelines

Uncompromising Accuracy & Detail in BIM Data

Facilitating Code Compliance & Constructibility
Special offer:
GET a FREE 3D BIM Model
with Your Shop Drawing Order!
Streamline your construction projects with All-City Sketchers!
Learn about the special offer:
Learn about the special offer:

By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
Limited Time Offer. Project Restrictions Apply. See full details: all-city-sketchers.com/bimoffer
Limited Time Offer. Project Restrictions Apply. See full details: all-city-sketchers.com/bimoffer
FEATURED Projects
On this project we’ve drafted, fabricated and installed ductwork. Another achievement that we were able to successfully coordinate routings for all trades for the entire building.
500 Main Street is a 26-story tower in the heart of Downtown, New Rochelle, NY, which consists of studio, one and two-bedroom units above a five-story parking garage.
500 Main Street is a 26-story tower in the heart of Downtown, New Rochelle, NY, which consists of studio, one and two-bedroom units above a five-story parking garage.
Apartments
New York
26 floors



We are proud to have successfully executed the BIM process consisting of BIM Modeling and Coordination throughout the project:
• ductwork layout for SC (2-5th floors and 7-18th floors);
• sketching and BIM coordination.
50 Hudson Yards is a 58-story office development that forms an integral part of the new Hudson Yards district on the western edge of Manhattan.
The building occupies an entire city block, providing almost 3 million square-feet of flexible office space along with retail facilities at street level.
• ductwork layout for SC (2-5th floors and 7-18th floors);
• sketching and BIM coordination.
50 Hudson Yards is a 58-story office development that forms an integral part of the new Hudson Yards district on the western edge of Manhattan.
The building occupies an entire city block, providing almost 3 million square-feet of flexible office space along with retail facilities at street level.
Commercial
New York
14 floors



The scope of this hospitality project consisted of creating a BIM design model, coordination and collaboration of the architectural, structural and MEP designs.
Effective clash detection during the coordination process provided valuable insights for designers to make the necessary changes. Сompleted work:
• ductwork and mechanical piping layout;
• sketching and BIM coordination.
250 Fifth Avenue is an upcoming 23-story, 230-foot tall building in Midtown.
Main idea to merge old 7 story building and new 25 story building in one.
Effective clash detection during the coordination process provided valuable insights for designers to make the necessary changes. Сompleted work:
• ductwork and mechanical piping layout;
• sketching and BIM coordination.
250 Fifth Avenue is an upcoming 23-story, 230-foot tall building in Midtown.
Main idea to merge old 7 story building and new 25 story building in one.
Commercial
New York
135 453 sq ft



We have worked out ventilation systems for the entire building:
• ductwork layout for the building;
• sketching and BIM coordination.
451 Tenth Avenue is a 587-foot-tall residential skyscraper. The 45-story structure is located on a 17,280-square-foot L-shaped lot at the corner of 10th Avenue and West 35th Street, just north of Hudson Boulevard‘ 66, Bjarke Ingels.
• ductwork layout for the building;
• sketching and BIM coordination.
451 Tenth Avenue is a 587-foot-tall residential skyscraper. The 45-story structure is located on a 17,280-square-foot L-shaped lot at the corner of 10th Avenue and West 35th Street, just north of Hudson Boulevard‘ 66, Bjarke Ingels.
Apartments
New York
45 floors



DISCOVER MORE bim projects
One of the biggest office towers in New York City.
A 78-story commercial building
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings: Sheet metal
A 78-story commercial building
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings: Sheet metal
The flagship complex of Pace University in New York City.
Size: 2,000 sq ft. Public
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Size: 2,000 sq ft. Public
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings: Sheet metal
33 Liberty Street. Located in the Financial District of Manhattan. Size: 49,440 sq ft. Commercial
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Property located in the Lower East Side neighborhood in Manhattan. The condominium has a total of 14 units. Size: 39,188 sq ft. Residential
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
The 250 Fifth Avenue, a 24-story ground-up 230-foot tall building located in Midtown. Size: 135,453 sq ft. Commercial
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
700 Washington Boulevard, "The Wave" 24-story tower and a 12-story building, with a five story connecting structure in between. Residential
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
301 East 80th Street. Condominium with 30 floors.
Size: 259,539 sq ft. Residential
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
Size: 259,539 sq ft. Residential
Scope: BIM Coordination, Shop drawings:
Sheet metal, Mechanical Piping
One Chase Manhattan Plaza, a 60-story building in the Financial District of Manhattan. Commercial
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Union Theological Seminary
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
Scope: Shop drawings: Sheet metal
FAQ
BIM services, short for Building Information Modeling services, represent a comprehensive set of tools and technologies used in the construction industry to streamline the entire project lifecycle. It involves the creation and management of a digital model that includes both the physical and functional aspects of a building or infrastructure project.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) works by utilizing advanced software and technologies to create a virtual representation of a building or infrastructure project. It involves the integration of various data sources and disciplines, including architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, into a central 3D model.
At the core of BIM is the collaborative sharing of information among project stakeholders. Each stakeholder, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers, contributes their expertise and information to the BIM model. This shared model serves as a single source of truth, allowing for seamless collaboration, coordination, and efficient decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
To create a BIM model, the process typically involves several steps. These include capturing accurate measurements through techniques such as 3D scanning, creating digital representations of the project components, integrating and analyzing data, identifying clashes and conflicts, generating construction drawings and documentation, and facilitating ongoing maintenance and operation. BIM enables real-time updates and modifications, providing stakeholders with an up-to-date and accurate representation of the project at any given time.
Overall, BIM improves construction processes by enhancing visualization, enabling clash detection and coordination, encouraging collaboration, and facilitating efficient project management. It provides a holistic and intelligent approach to construction, supporting better decision-making, cost savings, reduced errors, and ultimately, successful project delivery.
At the core of BIM is the collaborative sharing of information among project stakeholders. Each stakeholder, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers, contributes their expertise and information to the BIM model. This shared model serves as a single source of truth, allowing for seamless collaboration, coordination, and efficient decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
To create a BIM model, the process typically involves several steps. These include capturing accurate measurements through techniques such as 3D scanning, creating digital representations of the project components, integrating and analyzing data, identifying clashes and conflicts, generating construction drawings and documentation, and facilitating ongoing maintenance and operation. BIM enables real-time updates and modifications, providing stakeholders with an up-to-date and accurate representation of the project at any given time.
Overall, BIM improves construction processes by enhancing visualization, enabling clash detection and coordination, encouraging collaboration, and facilitating efficient project management. It provides a holistic and intelligent approach to construction, supporting better decision-making, cost savings, reduced errors, and ultimately, successful project delivery.
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is of utmost importance in the construction industry due to its remarkable ability to improve project efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration among project stakeholders.
One of the key reasons why BIM is important is its ability to provide a comprehensive and accurate digital representation of the project before construction begins.
This detailed 3D model allows for better visualization, enabling stakeholders to gain a clear understanding of the design, layout, and functionality of the building. This visualization aids in identifying and resolving potential clashes or conflicts between various systems, such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing, before they become costly issues during the construction phase.
Furthermore, BIM promotes effective collaboration and communication among designers, architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. By working on a shared platform, project teams can access and modify the same model, exchanging information and making real-time updates.
This collaborative approach enhances coordination and reduces errors and rework, ultimately leading to improved project timelines and cost savings. BIM also allows for accurate quantity takeoffs and cost estimations, further optimizing the project budget. Overall, the importance of BIM cannot be understated in its ability to drive efficiency, mitigate risks, and improve construction outcomes.
One of the key reasons why BIM is important is its ability to provide a comprehensive and accurate digital representation of the project before construction begins.
This detailed 3D model allows for better visualization, enabling stakeholders to gain a clear understanding of the design, layout, and functionality of the building. This visualization aids in identifying and resolving potential clashes or conflicts between various systems, such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing, before they become costly issues during the construction phase.
Furthermore, BIM promotes effective collaboration and communication among designers, architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. By working on a shared platform, project teams can access and modify the same model, exchanging information and making real-time updates.
This collaborative approach enhances coordination and reduces errors and rework, ultimately leading to improved project timelines and cost savings. BIM also allows for accurate quantity takeoffs and cost estimations, further optimizing the project budget. Overall, the importance of BIM cannot be understated in its ability to drive efficiency, mitigate risks, and improve construction outcomes.
Special offer:
GET a FREE 3D BIM Model
with Your Shop Drawing Order!
Streamline your construction projects with All-City Sketchers!
Learn about the special offer:
Learn about the special offer:

By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy
Limited Time Offer. Project Restrictions Apply. See full details: all-city-sketchers.com/bimoffer
Limited Time Offer. Project Restrictions Apply. See full details: all-city-sketchers.com/bimoffer
Book a Call
By clicking the button you agree to our Privacy Policy




